Diamond
Single Layer
PBEsol
Relaxation Quality Parameters
| Step
|
Displacement q (b1, b2, b3)
|
Build-in Factor
|
Total Energy (eV/atom)
|
Total Force (eV/Å/atom)
|
Cell Pressure (GPa)
|
Resulting Mean ω1 (cm-1)
|
Lowest ω (cm-1)
|
| 0
|
-
|
-
|
-90.40389544
|
6.90e-05
|
0.010
|
-0.493665
|
-63.177
|
| 1
|
9 (-0.526 0.254 0.000)
|
1.0
|
-90.33443035
|
4.50e-05
|
0.000
|
-0.718166
|
-59.031
|
| 2
|
3 (-0.001 -0.513 0.000)
|
1.0
|
-90.40389384
|
6.00e-05
|
-0.000
|
-0.597389
|
-64.901
|
| 3
|
9 ()
|
1.0
|
-90.39834846
|
4.50e-05
|
-0.010
|
-13.822794
|
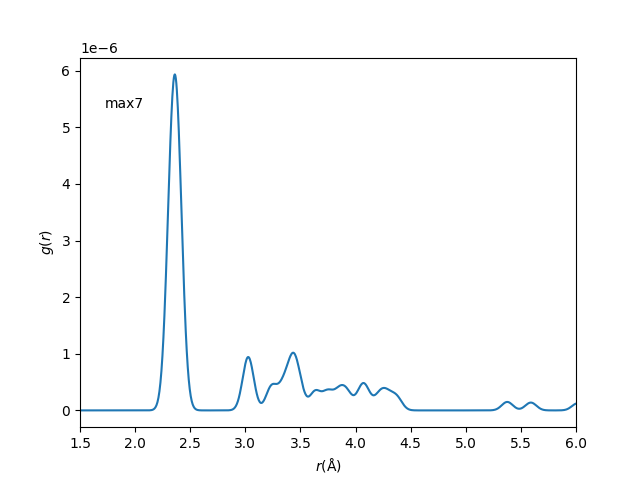
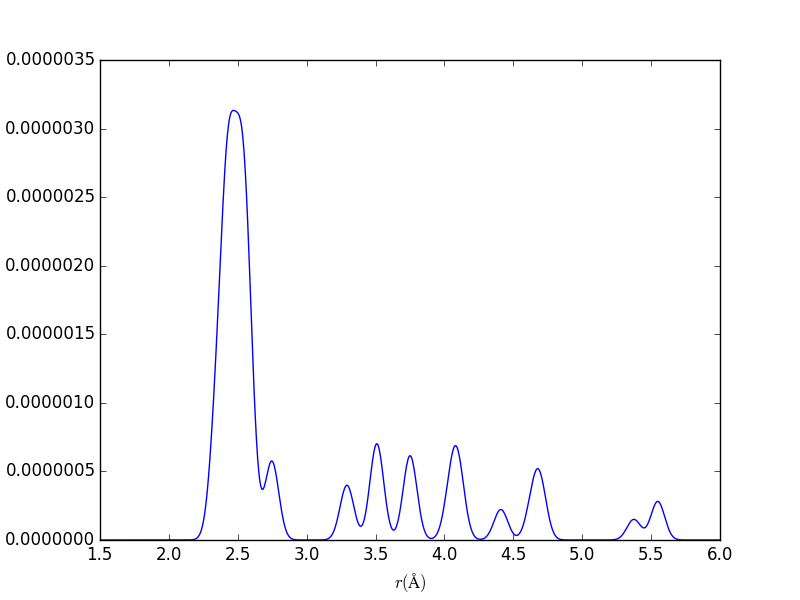
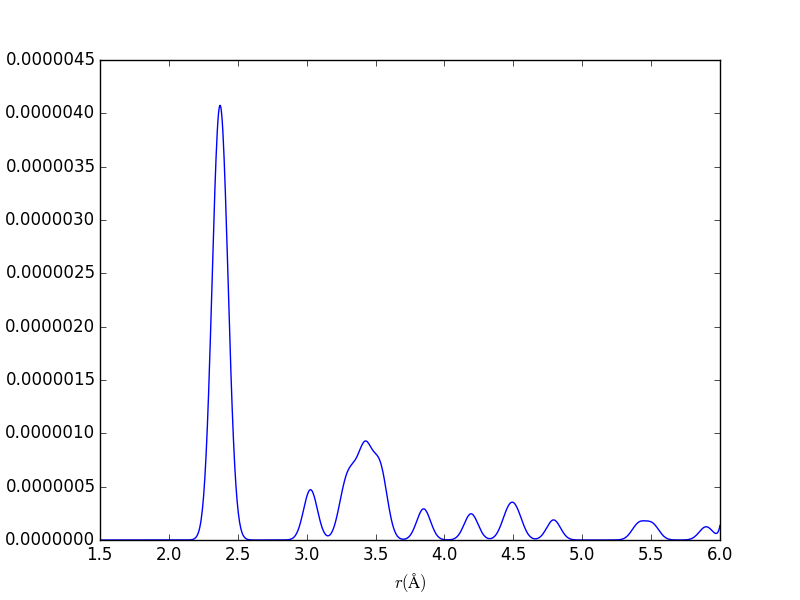
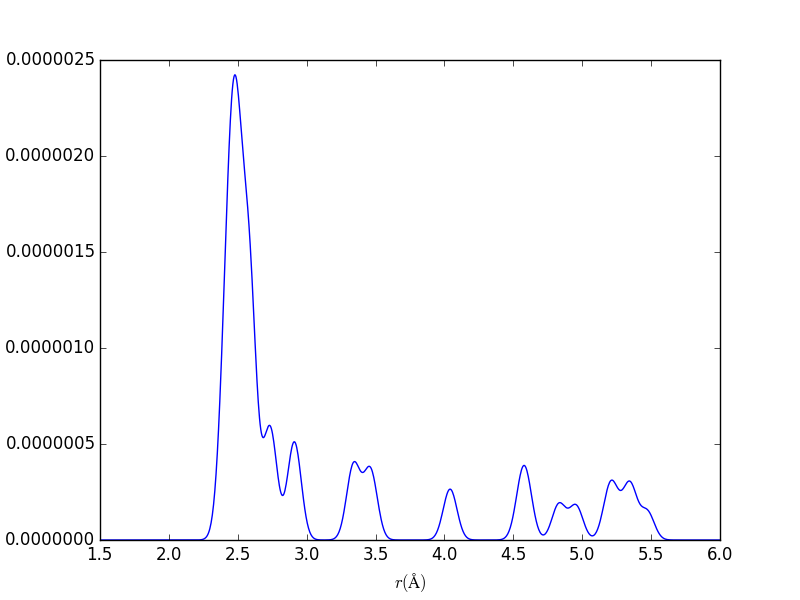
Pair Distribution Functions
aPBEsol = 5.495 Å ; rNN, bulk, PBEsol = 2.379 Å
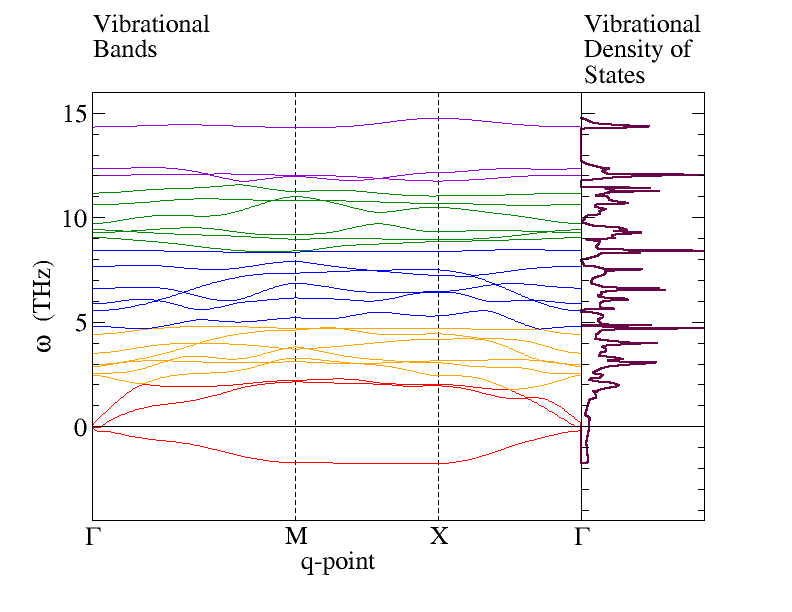
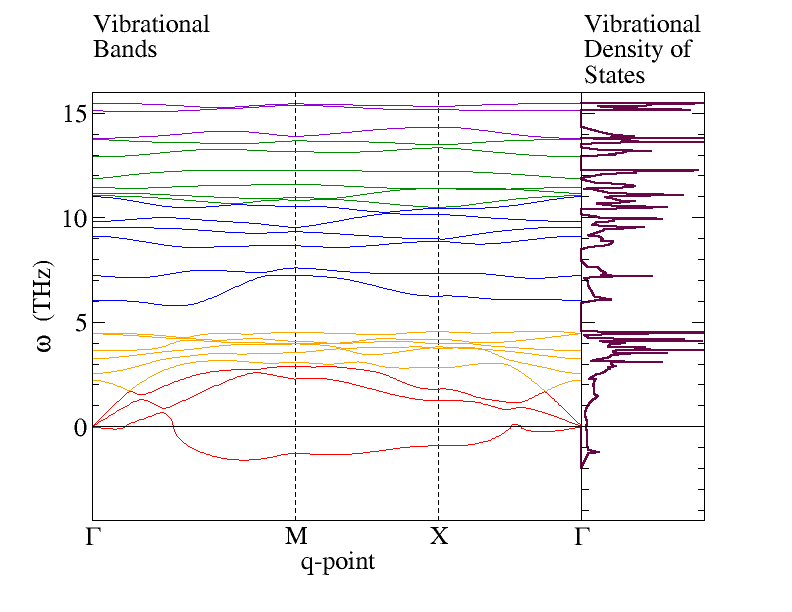
Phonon Bands and Density of States
Relaxation Procedure
- Create slab using copies of bulk structure coordinates
- Relax slab using loose total force convergence (~10-3 Ry bohr)
- Vary celldm(1) by fixed perentage around loosely relaxed slab and relax each new structure to tighter total force convergence (~10-4 Ry bohr)
- Relax the minimum-energy structure from that step to the tightest force convergence (~10-5 Ry bohr)
- Vary celldm(3) around the relaxed minimum energy structure and relax the in-plane (x & y) coordinates only
- Fit the equation of state to these energies and volumes